became the fourth deepest Polish cave. Another interesting discoveries were achieved in Snieżna Studnia by cavers from Zakopane and Jordanów, Jaskinia Wielka Snieżna by cavers from Bielsko-Biała and in Jaskinia Zimna by cavers from Kraków. There were also other significant though smaller finds in a number of Tatra caves. The caves: Jaskinia Wielka Snieżna and Jaskinia Kasprowa Niznia became goals of cave divers (see the article by Szerszeń).
All Tatra caves are situated in the Tatrzański National Park and caving activities are strictly limited by the Park authorities. Only six caves are open for tourists. For visiting other caves special permission is needed.
Pieniny Klippen Belt (Pieniński pas skałkowy)
I this area resistent Mesosoic limestone build up isolated klippen surrounded by non-karst rocks. There are more than 90 caves in this area. Although all these caves are in limestones, most of them are of non-karst (pseudokarst) origin. The longest cave is Jaskinia w Ociemnem, which is 196 m long and 47.5 m deep.
Beskidy Mts. (Beskidy)
The Beskidy Mts. are built of Cretaceous-Paleogene flysch - sandstones and shales.More than 811 caves are known there, all of non-karst (pseudokarst) origin with sandstones as the host rocks. They originated by gravitational movements of rocks along crcks. The longest cave is Jaskinia w Trzech Kopcach (1228 m) in the Beskid Śląski Mts. and the deepest is Diabla Dziura w Bukowcu (-42.5 m) in the Pogórze Rożnowskie foothills.
Kraków-Wieluń Upland (Wyżyna Krakowsko-Wieluńska)
This area occupies about 2500 km2. Now-ada/s there are more than 1800 known caves. Almost all of them are developed in Upper Jurassic limestones. Only a few occur in Lower Carboniferous limestones and Middle Triassic limestones and dolomites. ![]()
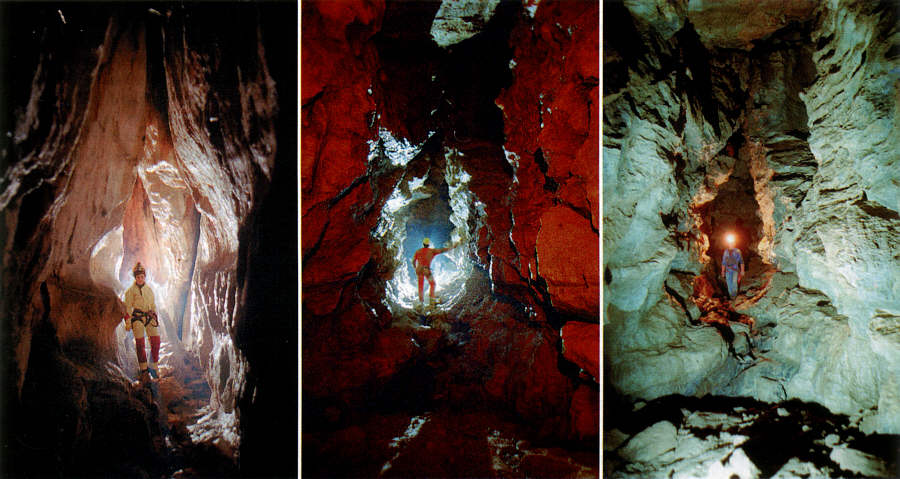
Jaskinia Groby (Tatra Mts) |
Jaskinia Kozia (Tatra Mts) |
Jaskinia Kozia (Tatra Mts) |
ph. Jakub Nowak